Exploring the Nature of the Au-S Bond in Thiol-Functionalized Gold
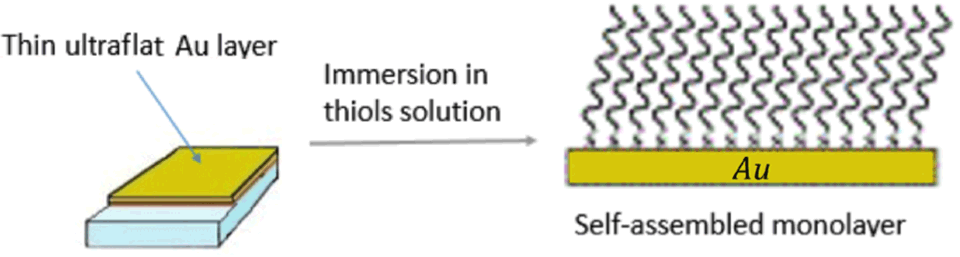
The adsorption of self-assembled monolayers (SAMs) on metals and metal oxides is a very simple and versatile method for tailoring surface properties. In fact, molecules that form SAMs anchor spontaneously onto the surface via a functional group that has specific affinity for the surface atoms, while the interaction between hydrocarbon chains determines the organization of the adsorbed monolayer in an ordered structure, without requiring any external driving force. One of the most studied systems consists of SAMs of thiols on gold, which can be obtained by simply soaking a gold surface in an ethanolic solution of thiols.
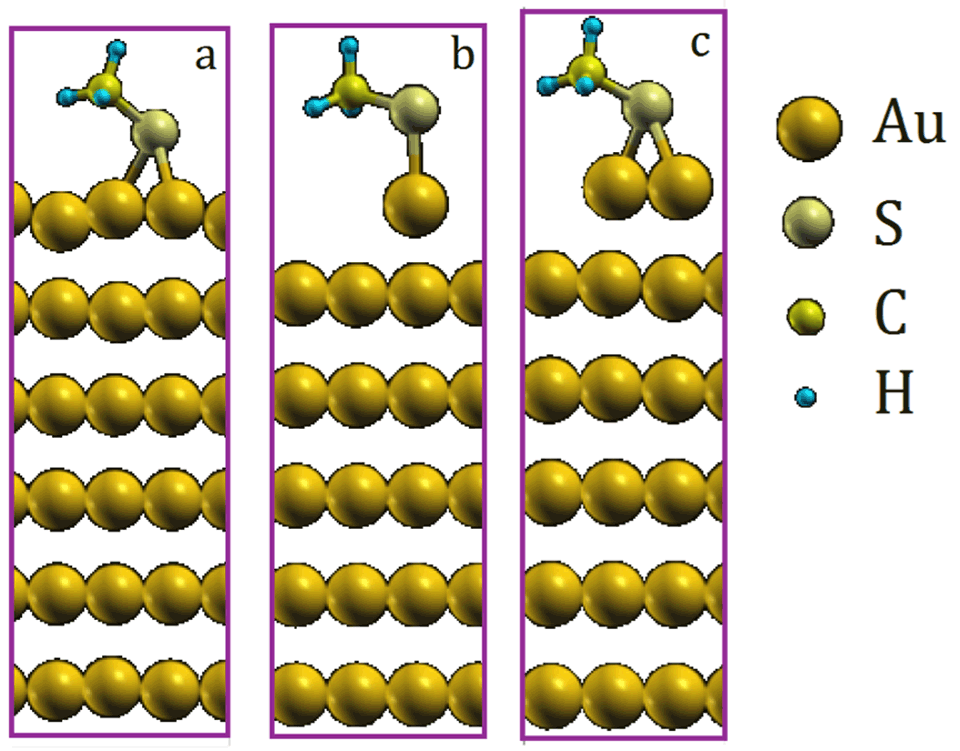
Surprisingly, although many characteristics of these thiol-based SAMs on gold are theoretically and experimentally well known, there’s still a lack of knowledge about the nature of the Au-S bond1. The aim of this project is the determination of the adsorption site and the local adsorption geometry at the S-Au interface. The study is carried out by means of angle resolved X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (ARXPS) measurements in combination with density functional theory (DFT) calculations. The binding energy (BE) of the core electrons in the Au(111) surface atoms is measured experimentally by ARXPS on thiol-functionalized samples, and it is compared to the energy calculated by DFT for core electrons in model systems reproducing different possible geometries. The effect of different substituents in the adsorbed molecules is also investigated.
In order to maximize the information coming from the proximity of the interface while reducing the bulk contribution, SAMs are adsorbed on thin Au films (thickness < 15 nm). Moreover, the surface of these gold films is ultraflat (roughness < 1 nm), because they are obtained through a template stripping method.
Work co-supervised by
Prof. Antonella Rossi, ETH and Università degli Studi di Cagliari, Italy
In cooperation with
Prof. W.T. Tysoe, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, USA
Prof. M.T. Weinert, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee, USA
References
(1) Love, J. C.; Estroff, L. A.; Kriebel, J. K.; Nuzzo, R. G.; Whitesides, G. M. Self-Assembled Monolayers of Thiolates on Metals as a Form of Nanotechnology. Chemical Reviews 2005, 105, 1103-1170.